
Leading Companies and Their Services
The global landscape of international shipping logistics is dominated by a handful of powerful companies, each with a unique history, specialization, and geographic reach. Understanding their strengths and service offerings is crucial for businesses seeking efficient and reliable international transportation solutions. This section will profile several leading companies and analyze the comparative strengths of three major players.
The international shipping logistics industry is highly competitive, with companies constantly striving to improve efficiency, expand their service offerings, and adapt to evolving global trade patterns. Technological advancements and the increasing demand for transparency and traceability have further shaped the industry’s evolution. These factors have led to the emergence of several large, globally integrated logistics providers.
Leading International Shipping Logistics Companies
Several companies stand out as leaders in the international shipping logistics market. Below is a brief overview of five prominent players, highlighting their history, specializations, and geographic reach. It’s important to note that the specific services and geographic coverage can vary over time.
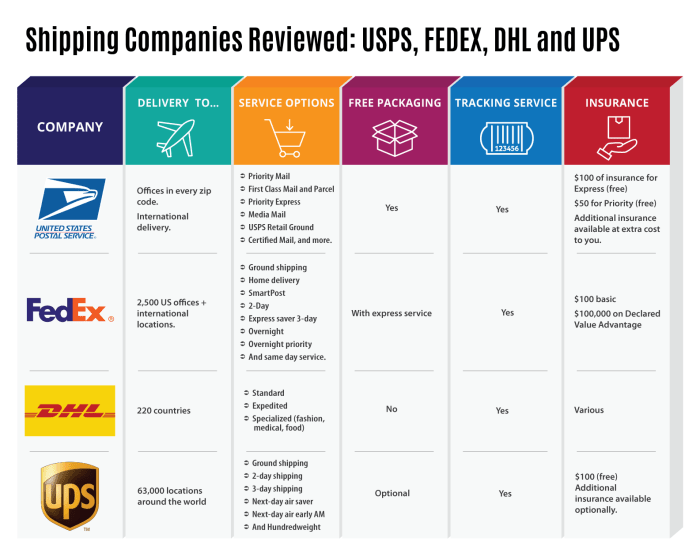
- DHL: Founded in 1969, DHL is a global giant offering a comprehensive suite of services, including air freight, ocean freight, road freight, and contract logistics. Its global network spans virtually every country, making it a leading choice for businesses with worldwide operations. DHL is known for its advanced technology and robust tracking systems.
- FedEx: Established in 1971, FedEx is another industry behemoth specializing in express delivery services, air freight, and ground transportation. Its extensive air and ground network provides fast and reliable delivery options globally. FedEx’s strong focus on technology and customer service is a key differentiator.
- UPS: Founded in 1907, UPS initially focused on messenger services before expanding into a global logistics powerhouse. UPS provides a comprehensive range of services including air freight, ocean freight, ground transportation, and supply chain solutions. They are known for their efficient operations and global reach.
- Kuehne + Nagel: This Swiss company, founded in 1890, is a leading provider of sea freight, air freight, contract logistics, and overland services. Kuehne + Nagel is known for its strong focus on providing integrated logistics solutions and its expertise in various industry sectors.
- DB Schenker: A German logistics company with a long history, DB Schenker offers a broad range of services including land transport, air freight, sea freight, and contract logistics. It leverages its extensive rail network in Europe and its global network for comprehensive logistics solutions.
Comparative Analysis of Three Major Players: DHL, FedEx, and UPS
DHL, FedEx, and UPS are three major players offering overlapping but distinct service portfolios. A comparison across key areas highlights their competitive strategies.
| Feature | DHL | FedEx | UPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warehousing | Extensive global network of warehouses offering various value-added services. | Offers warehousing solutions integrated with their express delivery network, focusing on speed and efficiency. | Provides a wide range of warehousing options, including temperature-controlled facilities and specialized handling. |
| Customs Brokerage | Provides comprehensive customs brokerage services globally, navigating complex regulations. | Offers customs brokerage services integrated with their transportation solutions for seamless international shipping. | Offers customs brokerage services worldwide, supporting clients with import and export compliance. |
| Supply Chain Management | Offers end-to-end supply chain management solutions, including planning, procurement, and optimization. | Provides supply chain management services focusing on speed and visibility, leveraging technology for real-time tracking. | Offers comprehensive supply chain solutions, including consulting, technology, and logistics services. |
Technology Used by Top Logistics Companies
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency and tracking shipments for top logistics companies. The adoption of advanced technologies is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in this dynamic industry.
- GPS Tracking: Real-time tracking of shipments via GPS devices provides visibility and enhances security.
- RFID Technology: Radio-frequency identification tags allow for automated tracking and identification of goods throughout the supply chain.
- Blockchain Technology: Improves transparency and security by creating a tamper-proof record of transactions and shipment movements.
- AI and Machine Learning: Used for predictive analytics, route optimization, and improved forecasting to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzing vast amounts of data to identify trends, improve decision-making, and optimize operations.
- Cloud Computing: Enables access to data and applications from anywhere, enhancing collaboration and improving responsiveness.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices and sensors across the supply chain for real-time monitoring and data collection.
Future of International Shipping Logistics
The international shipping logistics industry is on the cusp of significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental concerns, and evolving customer expectations. The next five years promise to be a period of rapid change, reshaping how goods are moved across borders and impacting the competitive landscape. Companies that embrace innovation and adapt to these changes will thrive, while those that remain stagnant risk being left behind.Technological innovations will play a pivotal role in this transformation.
The integration of new technologies will enhance efficiency, transparency, and sustainability across the entire supply chain.
Technological Innovations Transforming International Shipping
Several technological advancements are poised to revolutionize international shipping logistics within the next five years. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will optimize routing, predict disruptions, and improve cargo handling. Blockchain technology offers the potential for increased transparency and security in tracking goods, streamlining documentation processes, and reducing the risk of fraud. The Internet of Things (IoT) through the use of smart sensors on containers and vessels will provide real-time data on cargo location, condition, and environmental factors, enabling proactive problem-solving and improved decision-making.
Furthermore, the adoption of autonomous vessels and drones is expected to increase efficiency and reduce operational costs. For example, Maersk is already investing heavily in autonomous vessel technology, aiming to integrate it into its fleet in the coming years. This signifies a substantial shift towards automation within the industry.
Factors Influencing the Sustainability of International Shipping Practices
The environmental impact of international shipping is a growing concern, prompting stricter regulations and increased pressure on companies to adopt sustainable practices. Carbon emissions from ships are a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, leading to international agreements like the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap and its ongoing efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from shipping. Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, requiring companies to invest in cleaner fuels, more efficient vessels, and improved waste management systems.
Moreover, consumer demand for sustainable products and ethical sourcing is also pushing companies to adopt environmentally friendly practices. Failure to address these sustainability challenges will result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
Characteristics of a Future-Proof International Shipping Logistics Company
A “future-proof” international shipping logistics company will be characterized by its seamless integration of technology, unwavering commitment to sustainability, and customer-centric approach. This means leveraging AI, ML, blockchain, and IoT to optimize operations, enhance transparency, and provide real-time visibility to customers. It will also necessitate investing in alternative fuels, energy-efficient vessels, and sustainable packaging solutions to minimize its environmental footprint.
Furthermore, a future-proof company will prioritize building strong customer relationships by providing personalized services, proactive communication, and seamless end-to-end solutions. Companies such as DHL and FedEx are already demonstrating leadership in these areas through their investments in sustainable practices and technological innovations. Their success serves as a blueprint for others seeking to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Case Studies

Successful international shipping logistics strategies often involve overcoming significant challenges and leveraging technological advancements. Examining real-world examples provides valuable insights into best practices and effective approaches. The following case studies highlight successful strategies and the impact of technological innovation in the industry.
DHL’s Response to the Suez Canal Blockage
In March 2021, the Ever Given container ship became wedged in the Suez Canal, causing a major disruption to global shipping. DHL, a leading global logistics provider, faced significant challenges in rerouting shipments and managing client expectations. Their successful response involved a multi-pronged strategy. First, they leveraged their extensive global network to identify alternative routes and modes of transportation.
This included utilizing air freight for time-sensitive shipments and rerouting sea freight through alternative canals and ports. Second, DHL proactively communicated with clients, providing transparent updates on shipment status and potential delays. Third, their advanced technology platforms allowed for real-time tracking and monitoring of shipments, enabling efficient decision-making and proactive problem-solving. The company’s ability to adapt quickly, utilize diverse transportation modes, and maintain open communication with clients mitigated the impact of the blockage, showcasing their robust contingency planning and operational resilience.
Maersk’s Implementation of AI-Powered Optimization
Maersk, a global shipping giant, has significantly improved efficiency and profitability through the implementation of AI-powered optimization tools. These tools analyze vast amounts of data, including weather patterns, port congestion, and vessel capacity, to optimize shipping routes, predict potential delays, and improve fuel efficiency. For example, their AI algorithms can identify optimal vessel speeds based on real-time conditions, minimizing fuel consumption and reducing carbon emissions.
The implementation of these technologies has led to significant cost savings, improved on-time delivery rates, and enhanced overall operational efficiency. This illustrates the transformative potential of technology in streamlining international shipping logistics.
Successful Partnerships in International Shipping
The following table showcases successful collaborations between international shipping logistics companies and other businesses within the supply chain. These partnerships demonstrate the synergistic benefits of collaboration and integrated approaches to logistics.
| Company A | Company B | Partnership Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maersk | IBM | Technology Integration | Improved supply chain visibility, enhanced predictive analytics, optimized logistics operations. |
| DHL | Amazon | Last-Mile Delivery | Expanded delivery network, faster delivery times, improved customer satisfaction. |
| FedEx | Walmart | Warehousing and Distribution | Reduced warehousing costs, improved inventory management, streamlined distribution processes. |
| UPS | Nike | Global Supply Chain Management | Enhanced supply chain visibility, improved inventory control, reduced transportation costs. |




